Plastic molding is an essential manufacturing process, transforming raw plastic materials into various products that are integral to many industries. From everyday household items to highly specialized automotive components, different molding techniques cater to a wide range of applications. In this guide, we explore several key types of plastic molding, outlining their features, properties, and uses to help you better understand which method may suit your needs.
Injection Molding
Injection molding is one of the most widely used plastic manufacturing techniques, especially for creating high-volume, precision parts. This process involves melting plastic pellets and injecting the molten plastic into a mold cavity. The material then cools and hardens into the desired shape.
Known for its versatility, injection molding is suitable for producing parts with complex shapes and intricate designs. It ensures high consistency in size and dimensions, making it ideal for precision products. The process is compatible with a wide range of plastics, from thermosetting to thermoplastic polymers, allowing manufacturers to create customized parts with different material properties.
Injection molding is commonly used in the automotive, electronics, and medical industries. Products like car parts, medical devices, bottle caps, and electronic casings are often made using this method. Its ability to produce high volumes at a low cost per unit makes it an economical choice for mass production.
Blow Molding
Blow molding is a technique used to produce hollow, thin-walled parts. In this process, molten plastic is extruded into a tube, and compressed air is blown inside to expand the plastic and shape it against the mold’s walls.
Blow molding is ideal for creating uniform wall thickness in hollow products. The process is simple and fast, which makes it highly efficient for high-volume production. It also offers the flexibility to use different types of plastic, including high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polypropylene (PP).
Common applications include plastic bottles, fuel tanks, and containers. Blow molding is especially useful in the pharmaceutical and health & beauty industries for making bottles and vials. Its ability to produce large quantities quickly makes it a go-to for packaging solutions.
Compression Molding
Compression molding involves placing heated plastic into a mold, which is then compressed to shape the material. The plastic is cured with heat, cooled, and then removed from the mold.
This method is known for producing highly durable and strong parts. It’s particularly effective for creating larger and thicker components, and it supports a range of advanced plastic materials, such as thermosetting resins and fiberglass. Compression molding is less suited for intricate designs due to the limitations of mold compression.
Compression molding is widely used in the automotive industry for parts like bumpers and electrical insulators. Other applications include body armor, household appliances, and even fasteners for clothing. Its ability to create robust components makes it ideal for industrial and heavy-duty uses.
Extrusion Molding
Unlike other molding processes, extrusion molding continuously forces melted plastic through a die to form a specific cross-sectional shape. The plastic is pushed through the die by a screw, and the final product is formed as it exits.
Extrusion molding is best for producing long, cylindrical shapes with a uniform cross-section. It’s a continuous process, allowing for the efficient production of items like pipes, tubes, and profiles. The die can be customized to create various shapes, such as T-sections or L-sections, making it versatile for specific applications.
Common products made through extrusion molding include PVC piping, straws, plastic tubing, and cable insulation. Its ability to create consistent, lengthy products makes it indispensable in the construction and plumbing industries.
Rotational Molding
Rotational molding, or rotomolding, is used for making large, hollow objects. A mold is filled with powdered plastic, which is then heated and rotated, causing the plastic to coat the inside walls evenly. Once cooled, the product is removed from the mold.
This process is highly efficient and eco-friendly, as it produces very little waste, and any excess material can often be reused. Rotomolding creates products with even wall thickness, and the absence of seams in the final product enhances its strength and durability.
Rotomolding is ideal for producing large, hollow items like storage tanks, playground equipment, and kayaks. Its ability to create seamless, robust products makes it especially suitable for watercraft and outdoor furniture.
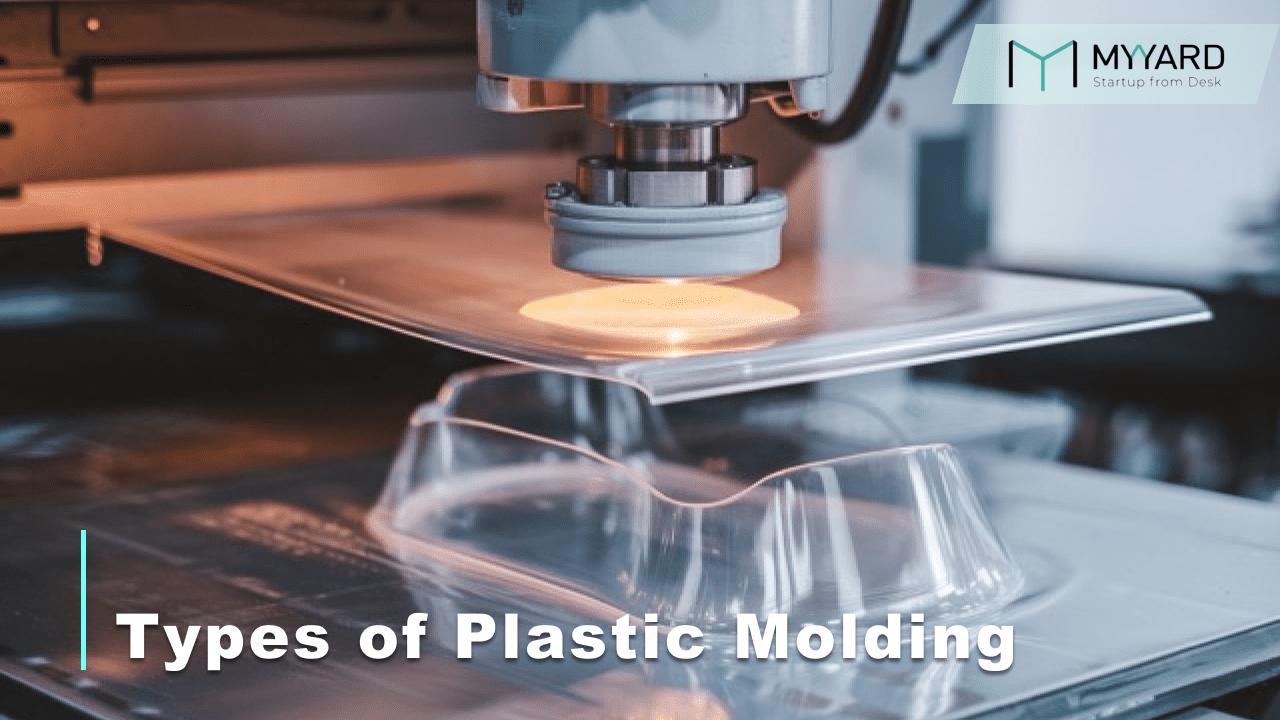
Thermoforming
Thermoforming is a widely used plastic molding technique that involves heating a plastic sheet until it becomes pliable and then shaping it over a mold using a vacuum or pressure. The plastic sheet conforms to the mold’s shape and is subsequently cooled and trimmed to form the final product. Thermoforming is a broad term, including other methods. For example, vacuum forming uses vacuum suction to pull the heated plastic tightly over the mold, ensuring greater accuracy and detail, particularly for intricate or shallow designs.
Thermoforming is typically employed with thin plastic sheets, making it ideal for lightweight, cost-effective applications. It operates under relatively low pressure, keeping mold costs affordable compared to more complex molding methods. Vacuum forming, in particular, enhances design flexibility by using vacuum suction to create highly accurate mold reproductions, making it suitable for both detailed and larger, simple designs. The process is compatible with a variety of plastic materials, allowing for broad customization options in terms of strength, durability, and appearance.
Thermoforming, including vacuum forming, is commonly used for creating packaging materials such as trays, chocolate molds, resin molds, clamshell packages, and disposable cups. It is also utilized in automotive manufacturing for larger, flatter components like dashboard panels and interior liners. Due to its cost-efficiency and design flexibility, thermoforming is a popular choice in industries ranging from food packaging to automotive and consumer goods, where both lightweight and detailed product features are needed.
Harnessing the Power of Plastic Molding for Your Manufacturing Needs
Each plastic molding method offers unique advantages depending on the complexity, volume, and material requirements of your product. From simple packaging to intricate automotive components, selecting the right process can significantly enhance both product quality and production efficiency. Understanding these methods allows you to tailor your approach, ensuring precision, durability, and cost-effectiveness in your production.
Now, take your manufacturing to the next level with MY YARD’s Vacuum Forming Machine. Whether you're creating custom packaging, replicating molds, or experimenting with innovative designs, our desktop vacuum-forming technology offers rapid prototyping with unmatched flexibility. Perfect for small businesses, hobbyists, or manufacturers looking for an affordable yet efficient solution, our solution provides a streamlined path to high-quality, durable products.
Don’t miss the chance to turn your ideas into reality—contact MY YARD today and discover how our systems can revolutionize your production process!
Related Articles Suggested for You:
Thermoforming Explained: Process, Materials, and Applications
How to Make Resin Molds at Home: DIY Step-by-Step Guide
How to Make Chocolate with Molds DIY: Mold Types, Tips & More
What is Vacuum Forming: Steps, Materials, Types with Pros & Cons

No Comments